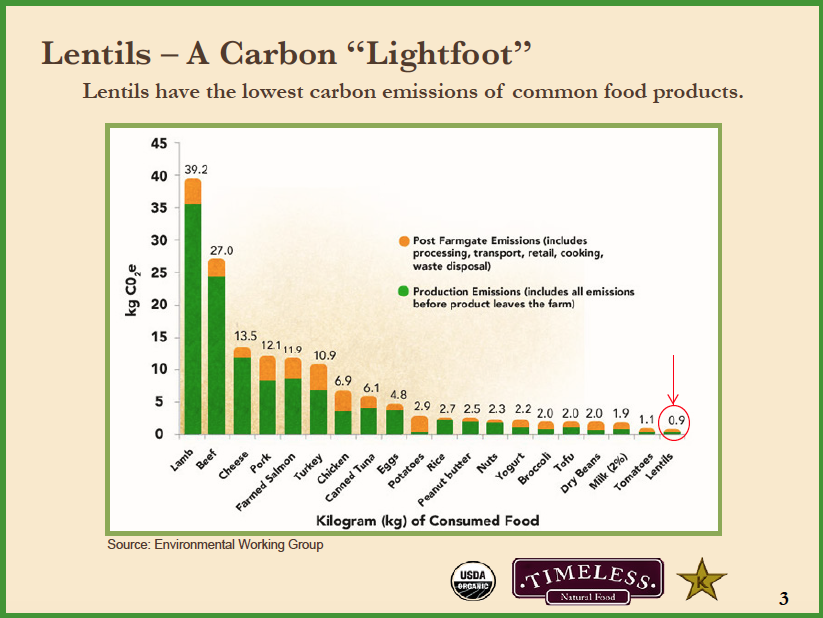
In contrast to meat, most of plant proteins’ emissions are generated after crops leave the farm (processing, transport, cooking and waste disposal). For example, post-farmgate emissions account for 65 percent of dry beans’ total emissions and 59 percent of lentils’ emissions, primarily because of the energy needed to cook them.